About
Purchased by the Cook County Forest Preserve District in 2003, Burnham Prairie Nature Preserve (BPNP) contains some of the highest quality wet prairie habitat in the state. Recently, the Army Corp of Engineers have completed restoration work on much of the east pond area. Plantings and herbicide application continues in the west pond area. A new parking lot and a modest trail were opened in 2014, significantly increase access to this site. As restoration work is ongoing, conditions change fairly frequently. Most notably, the water level is regularly manipulated to aid in the removal of invasive plants.
Getting There
BPNP is a confusing place to find; just outside of city limits in Burnham, IL. While the Torrence Avenue bridge is under construction (to be completed summer 2017) all traffic must arrive turning north on Torrence from State Street. From there, turn right (east) onto 140th Street then left (north) onto S Manistee Avenue. Finally, at the end of the street, turn right (east) 139st Street, which looks more like an alleyway. Proceed east about 30 yards and a metal swing gate marks the entrance.
How to Bird
Burnham Prairie has a few trails and no facilities. Late March – Early January are the most worthwhile times to visit. Late winter is mostly barren. As there is a great variety of habitat, it’s easiest to break-down each major trail/path:
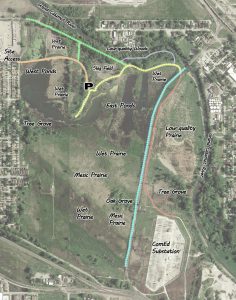
(Note: The trail colors only correspond to the above map. There are no trail markings at this preserve.)
Orange(Entry Road) – As you enter the preserve, you drive down a road bisecting the West Ponds allowing outstanding views of the bird life. Caspian Tern, herons, Pied-billed Grebes, and swallows can be expected spring through fall. Depending on the water level, this area can also be extraordinary for shorebirds. Besides the expected shorebirds, Black-bellied Plover, American Golden-Plover, Marbled Godwit and Willet have all been found here. Ducks will also frequent this area in migration but, not in numbers as seen in other parts of the preserve. The Wet Prairie in this area is a great place to see numbers of Wilson’s Snipe in the spring.
Yellow – For a short visit, this gravel path can usually give you a good idea as to what birds are around. This path has the best views of the East Ponds (scope helpful). Shorebirds can often be found wading around the north edges of the ponds. The Slag Field, dotted with a few isolated trees can occasionally produce some interesting birds (in the current year Northern Mockingbird has been found here repeatedly) and is frequented by woodpeckers and migrating Baltimore Orioles. Sparrows tend to load up along the prairie plants along this path. As you walk to the northeast portion of the path, around the small hill, you’ll approach the last stretch of path before the train tracks. This area can be a highly effective viewing station. To the distant south, you’ll be able to see herons hanging around the south edge of the West Pools, often in large numbers (high counts of Great Egret exceed 70). In the foreground, the wet prairie is very popular in the spring with teal, Wood Ducks, and the occasional rail. In the early summer, this area becomes loaded with Marsh Wren. To the north, the drop off to an oft-flooded depression is very popular with breeding Swamp Sparrow as well as House Wren. Eastern Kingbirds, Eastern Phoebes, and Blue-gray Gnatcatchers are abundant in season and commonly perch on the chain-link fence. Lastly, watching the woods in spring and fall can produce modest numbers of warblers and kinglets.
Blue – This trail consists of walking alongside the railroad tracks. These tracks are rarely used but, they do occasionally hold staging freight cars. A there-and-back walk along the tracks begins at the north end, alongside the Wet Prairie that is popular with Marsh Wren & Swamp Sparrows. In migration, Lincoln’s Sparrow can be found here. Continuing to walk south gives great morning views of the West Ponds with the sun at your back. Loads of ducks gather here although, it’s likely you’ll flush any birds that are in the closest pond. Telephone poles and the isolated trees along the tracks are popular perching spots for Red-tailed Hawks and American Kestrel; both of which breed in the area. When raptors aren’t around, these trees are very popular with migrating warblers and sparrows. Walking further to the south edge of the ponds Sedge Wren, Yellow Warblers, and Common Yellowthroat become the dominant bird. As you get closer to the Oak Grove, the calls of Willow Flycatchers become conspicuous, as well. In the Oak Grove area, Henslow’s Sparrow can be heard calling in spring. In the later summer, Red-headed Woodpeckers frequent this area as well as the Tree Grove east of the tracks. The quality of prairie plants in this area is outstanding. However, the birding is difficult and usually not very rewarding; rubber boots are a must and extreme care should be given not to trample the fragile vegetation. Most often, the birds that are observed from the tracks represent all the birds that can be found in this area. A walk around the Oak Grove can give a closer view of some of the prairie areas and better views of any birds they contain. A patch of bushes along the tracks, just north of the ComEd substation, are a favorite spot for migrating, under-story warblers (Northern Waterthrush, Ovenbird,…)
Green – This gravel access road leads through trees that border the Grand Calumet River. During migration, this is the best place in the preserve to find warblers, thrushes, vireo, and flycatchers. The area around the T-intersection is usually the hot spot. Continuing further west will generally give you more woodpeckers and sometimes lead to better views of shorebirds that are hanging out around the north end of the West Ponds.
Purple – More a worn footpath than a trail, useful to visit if you’re trying to add additional migrating passerines to your site list but, can be skipped. Often requires rubber boots and walking around broken glass and other decaying metal waste.
Red – Parallel to the tracks for most of the time and often flooded. Mostly popular with Red-winged Blackbirds and Killdeer. This path takes you onto ComEd property. Access to this area is allowed but, generally, only useful if you’re trying to get to the trees boarding the Grand Calumet River to the east.
Why this place is special
This preserve demonstrates the benefits of preservation and restoration. The remnant prairie that makes up the south half of the preserve is extraordinary for its plant diversity whereas the completed work on the north and west has created highly-productive bird habitat. This diversity provides sanctuary for both birds and other animals such as mink and coyote. In the summer breeding season, when most Chicago-area sites’ counts drop to 20-30 species, Burnham Prairie Nature Preserve can regularly produce species counts around 40-50. This preserve represents a great effort to return Common Gallinule, King Rail, and other extirpated species to the Calumet region.